Volts: Understanding Voltage and Its Role in Electrical Systems
Whether you’re choosing a generator, battery, or electrical appliance, one of the most important terms you’ll encounter is volts (V). But what exactly is voltage, and why does it matter in power systems?
Voltage is the driving force behind electricity, determining how power flows through a circuit. It affects everything from the efficiency of electrical devices to the performance of backup power systems like generators and UPS units.
In this guide, we’ll explain what volts are, how they work, their role in electricity, and how voltage impacts power generation, distribution, and consumption.
What Are Volts (V)?
A volt (V) is the unit of electrical potential difference or electromotive force in a circuit. It measures how much electrical pressure is available to push current through a conductor.
📌 Analogy: Think of voltage like water pressure in a pipe—the higher the voltage, the more electrical force is available to push electrons through a circuit.
Key Voltage Definitions
✅ Voltage (V) – The difference in electrical potential between two points in a circuit.
✅ Current (A – Amperes) – The flow of electric charge through a conductor.
✅ Resistance (Ω – Ohms) – The opposition to the flow of electricity in a circuit.
Ohm’s Law: The Relationship Between Voltage, Current, and Resistance
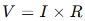
Where:
- V = Voltage (volts)
- I = Current (amperes)
- R = Resistance (ohms)
📌 If voltage increases, current increases—provided resistance remains constant.
Common Voltage Levels in Electrical Systems
Different electrical applications require specific voltage levels for safety and efficiency.
| Voltage Level | Application |
| 12V – 24V | Batteries, car electrical systems, low-power devices |
| 120V – 230V | Home appliances, power tools, residential power |
| 400V – 600V | Industrial machinery, commercial buildings |
| 11kV – 33kV | Power distribution networks, substations |
| 100kV+ | High-voltage transmission lines |
📌 Generators, transformers, and electrical grids must match the correct voltage levels to ensure safe and efficient power distribution.
Why Is Voltage Important?
Voltage affects how electrical systems function, how safely they operate, and how efficiently they transmit power.
- Determines Electrical Power Output
- The amount of power delivered to a device depends on voltage and current.
- Power (W) is calculated using:
P=V×IP
📌 Higher voltage allows for the same power with lower current, reducing energy loss.
- Affects Equipment Compatibility
- Electrical devices are designed for specific voltages (e.g., 120V, 230V).
- Using the wrong voltage can damage equipment or cause inefficient operation.
- Impacts Power Transmission Efficiency
- High-voltage transmission lines reduce energy loss over long distances.
- Industrial power systems use 400V+ for efficient machinery operation.
- Essential for Generator & Battery Performance
- Generators must provide stable voltage to prevent fluctuations and power surges.
- Batteries and inverters must supply the correct voltage to keep devices running efficiently.
📌 Matching voltage levels to equipment requirements ensures reliable performance and prevents damage.
AC vs. DC Voltage: What’s the Difference?
Electricity is supplied in two forms: Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC).
| Feature | AC Voltage | DC Voltage |
| Definition | Voltage alternates direction periodically | Voltage flows in one constant direction |
| Power Source | Generators, power grids | Batteries, solar panels, DC converters |
| Applications | Home electricity, industrial power | Electronics, electric vehicles, backup systems |
| Transmission | Efficient for long-distance power transmission | Limited to short-distance applications |
📌 AC voltage is used for large-scale power distribution, while DC voltage is preferred for electronics and energy storage.
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Voltage
Electrical systems are classified into single-phase and three-phase power supplies, depending on voltage requirements.
| Feature | Single-Phase | Three-Phase |
| Voltage | 120V – 230V | 400V – 600V |
| Number of Wires | 1 live + 1 neutral | 3 live + 1 neutral |
| Best For | Homes, small businesses | Industrial machinery, high-power applications |
| Efficiency | Less efficient for high loads | More efficient for heavy loads |
📌 Most homes use single-phase voltage, while industrial setups require three-phase voltage for heavy machinery.
How Voltage Affects Generators & Backup Power Systems
- Voltage Regulation in Generators
- Generators must maintain stable voltage output to prevent fluctuations and surges.
- Voltage regulators adjust output to match the load demand.
- UPS & Battery Backup Systems
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) convert battery voltage (12V/24V) into usable AC power (230V/120V).
- Ensuring correct voltage conversion prevents power failure in critical applications.
- Voltage Matching for Electrical Devices
- Plugging a 120V device into a 230V outlet can cause overheating and damage.
- Voltage converters or transformers adjust voltage levels for safe operation.
📌 Generators, UPS systems, and power backups must provide the correct voltage for stable operation.
Common Voltage Problems & Solutions
| Voltage Issue | Cause | Solution |
| Voltage Drop | Long cables, overloaded circuits | Use thicker cables, reduce load |
| Voltage Spikes & Surges | Lightning, faulty wiring, power grid switching | Install surge protectors, use voltage regulators |
| Overvoltage | Transformer faults, unstable power supply | Use automatic voltage stabilizers (AVS) |
| Undervoltage (Brownouts) | High demand, weak power grid | Use UPS or generators for backup power |
📌 Maintaining stable voltage is essential for safe and efficient electrical operation.
How to Measure Voltage
To check voltage levels in electrical systems, use a voltmeter or multimeter:
Step-by-Step Voltage Measurement
1️⃣ Set the Multimeter – Choose AC or DC voltage mode depending on the circuit.
2️⃣ Connect Probes – Place the red probe on the live wire and the black probe on neutral or ground.
3️⃣ Read the Voltage Display – The meter will show the current voltage level.
4️⃣ Compare with Standard Levels – Ensure voltage matches the expected range (e.g., 230V for home outlets).
📌 Regular voltage testing helps prevent power issues and equipment failures.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why is household voltage different in different countries?
Different regions adopted 120V or 230V systems based on historical standards and grid efficiency.
- Can voltage fluctuations damage electrical devices?
Yes, overvoltage or undervoltage can cause device failure, overheating, and reduced lifespan.
- What happens if I use the wrong voltage for a device?
Using too high a voltage can burn out circuits, while too low a voltage may prevent devices from working properly.
- How can I stabilize voltage in my home or business?
Use voltage stabilizers, surge protectors, or UPS systems to ensure steady power delivery.
- Do generators always provide stable voltage?
No. Generators require voltage regulators to prevent fluctuations and ensure stable output.
Conclusion
Voltage (volts – V) is a fundamental part of electrical systems, determining how power flows and how efficiently devices operate. From home electricity to industrial power grids, maintaining the correct voltage is essential for safety, efficiency, and performance.
Whether you’re using a generator, UPS, or battery backup system, ensuring the right voltage level helps prevent power failures, protect equipment, and optimize energy use.

