Evaluating Generator Efficiency Over Time
Definition
“The ratio of average load to the generating set power rating.”
Load factor is a key performance indicator in electricity generation, representing the ratio between the average electrical load a generator supplies and its maximum rated capacity over a specific period. It is a measure of how efficiently a generator is being utilised, and plays a central role in generator sizing, cost analysis, and energy management.
Why Load Factor Matters in Generator Operations
1. Indicates Utilisation Efficiency
-
A high load factor means the generator is consistently operating near its rated capacity, which is typically more economical.
-
A low load factor may suggest oversized equipment, underutilisation, or inefficient operation.
2. Affects Fuel Consumption & Cost
-
Generators running at low load factors may consume more fuel per kilowatt-hour produced, leading to higher operational costs.
3. Influences Maintenance Scheduling
-
Operating at consistent load levels reduces engine strain and component wear, supporting longer intervals between servicing.
Formula to Calculate Load Factor
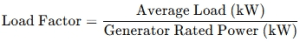
Example:
If a 500 kW generator delivers an average load of 300 kW:
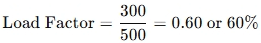
Interpreting Load Factor Values
| Load Factor (%) | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 80–100% | Excellent – generator is well-matched to load |
| 60–79% | Good – fairly efficient utilisation |
| 40–59% | Moderate – potential for optimisation |
| Below 40% | Poor – may indicate oversizing or inefficiency |
How to Improve Load Factor
-
Right-size the generator based on actual load profiles.
-
Implement automatic load management systems to reduce waste.
-
Use load banks to maintain minimum engine loading where necessary.
-
Regularly monitor and analyse energy usage patterns to spot inefficiencies.
Key Point
Load factor is an essential metric that helps evaluate how effectively a generator is used over time. By understanding and improving load factor, businesses can achieve better fuel efficiency, lower costs, and longer generator life.

