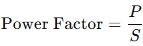The Total Power in an AC Generator System
Definition
“The product of current and voltage in an alternating current circuit which has a reactive element.”
Apparent power is the total power in an alternating current (AC) system, including both active power (real power) and reactive power. It is measured in volt-amperes (VA), kilovolt-amperes (kVA), or megavolt-amperes (MVA) and represents the total energy supplied by a generator before accounting for energy losses due to reactance.
Why Is Apparent Power Important in Generators?
1. Determines Generator Capacity
- Generators are rated in kVA (kilovolt-amperes) because they supply both active and reactive power.
- Helps ensure the generator can handle both real and reactive power demands.
2. Affects Power Factor & Efficiency
- A lower power factor means higher apparent power is needed to deliver the same active power.
- Improving power factor increases generator efficiency.
3. Impacts Electrical Load Performance
- Understanding apparent power helps in sizing transformers, cables, and generators.
- Reduces risks of overloading equipment.
Formula for Apparent Power
Apparent power (SS) is calculated as:
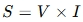
or
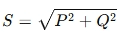
Where:
- S = Apparent Power (VA)
- P = Active Power (W) (Real power doing useful work)
- Q = Reactive Power (VAR) (Power stored and released by inductors/capacitors)
- VV = Voltage (Volts)
- II = Current (Amperes)
Apparent Power vs. Active & Reactive Power
| Type of Power | Symbol | Measured In | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active Power | P | Watts (W) | Does real work (lighting, motors, heating) |
| Reactive Power | Q | Volt-Amperes Reactive (VAR) | Supports inductive and capacitive loads |
| Apparent Power | S | Volt-Amperes (VA) | Total supplied power (P + Q) |
Power Factor Relationship:
A power factor closer to 1.0 (unity) means the generator is being used efficiently.
How to Optimise Apparent Power Usage in Generators
- Use Power Factor Correction Devices – Capacitors help improve efficiency.
- Ensure Proper Load Balancing – Reduces excess reactive power demand.
- Choose the Right Generator Size – Match the kVA rating to actual power needs.
- Monitor Power Factor Regularly – Helps maintain optimal generator efficiency.
Key Points
Apparent power represents the total power a generator supplies, combining both real and reactive power. Measured in VA, kVA, or MVA, it helps in sizing generators, transformers, and power systems efficiently. Proper power factor management ensures maximum efficiency and reliability in power generation.