Understanding Amps: Electrical Current in Diesel and Petrol Generators
If you’re dealing with diesel or petrol generators, you’ve probably come across the term amps (short for amperes). But what exactly are amps, and why do they matter when choosing or using a generator?
In simple terms, amps measure the amount of electric current flowing through a circuit. When you’re running power tools, household appliances, or industrial equipment with a generator, knowing the amp output is crucial. It helps ensure you’re supplying enough power without overloading your generator or damaging your devices.
In this article, we’ll break down what amps are, how they relate to volts and watts, and why understanding them is essential when dealing with diesel and petrol generators.
What Are Amps?
Amps (A) are the unit of measurement for electrical current, which is the flow of electrons in a circuit. Think of electricity like water in a hose:
- Voltage (V) is the pressure pushing the water through the hose.
- Amps (A) represent the amount of water flowing through the hose.
- Watts (W) indicate the total power being used, calculated by multiplying volts and amps.
In a generator, the number of amps it produces determines how much current can be supplied to electrical devices. If your generator doesn’t supply enough amps, your equipment won’t run properly—or at all!
The Basic Formula: Watts, Volts, and Amps
A simple formula helps explain the relationship between these electrical units:

For example, if you have a 240V generator and it produces 10 amps, then:

That means your generator can provide 2400 watts of power at 10 amps.
Why Are Amps Important in Generators?
Understanding amps is crucial when selecting or using a generator because it helps ensure you have enough power to run your appliances or machinery.
- Preventing Generator Overload
Every generator has a maximum amp output. Exceeding this limit can cause overheating, damage, or even failure. Knowing the amp draw of your devices helps avoid overloading your generator.
- Matching Generator Output to Power Needs
Different devices require different amounts of current. A small phone charger might only draw 1–2 amps, while a heavy-duty power tool could need 15–20 amps or more.
- Ensuring Safe Operation
Using a generator that supplies too many amps for a device can burn out electrical components. On the flip side, a generator with too few amps may not power the device at all.
Amps vs. Volts vs. Watts: What’s the Difference?
To better understand amps, let’s compare them with volts and watts:
| Term | Definition | Analogy |
| Amps (A) | Measures the flow of electrical current. | The amount of water flowing through a pipe. |
| Volts (V) | Measures electrical pressure. | The pressure pushing water through the pipe. |
| Watts (W) | Measures total power used. | The total energy transferred by the flowing water. |
Understanding these differences will help you choose the right generator size based on the amp needs of your equipment.
How Many Amps Does a Diesel or Petrol Generator Produce?
The amp output of a generator depends on its power rating (watts) and voltage.
Standard Amp Outputs for Common Generator Sizes
| Generator Size (Watts) | Voltage | Max Amps Output |
| 2,000W | 240V | 8.3A |
| 5,000W | 240V | 20.8A |
| 7,500W | 240V | 31.3A |
| 10,000W | 240V | 41.7A |
| 15,000W | 240V | 62.5A |
Most portable diesel and petrol generators produce between 10–50 amps, depending on their wattage and voltage.
To determine if a generator is right for you, add up the amp requirements of all the devices you need to run simultaneously.
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Generators: Amp Differences
Generators come in single-phase and three-phase configurations. Each type supplies amps differently:
- Single-Phase Generators
- Used in homes and small businesses.
- Supplies one continuous current.
- Typically operates at 240V in the UK.
- Three-Phase Generators
- Used in industrial and commercial applications.
- Delivers power in three alternating currents, which provides a more stable and efficient power supply.
- Commonly operates at 400V in the UK.
If you need high amp output for industrial equipment, a three-phase generator is often the best choice.
How to Calculate How Many Amps You Need
Before choosing a generator, you need to determine how many amps your devices require. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Check Device Ratings
Look at the label on each appliance or tool—it should list watts (W) or amps (A).
Step 2: Use the Watts-to-Amps Formula
If the label only lists watts, use this formula:
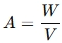
For example, if your power tool requires 2400W at 240V:
2400W÷240V = 10A
Step 3: Add Up All Amp Requirements
Total the amp requirements for all devices that will run at the same time.
Step 4: Choose a Generator with a Higher Amp Rating
Always choose a generator with slightly higher amp capacity than your total needs to avoid overload.
Common Amp Ratings for Household and Industrial Devices
| Device | Average Amps Required |
| LED Light Bulb | 0.1A |
| Laptop | 2A |
| Electric Kettle | 10A |
| Microwave | 12A |
| Power Drill | 15A |
| Air Compressor | 20A |
| Large Industrial Machine | 50A+ |
If you plan to run multiple devices, always check their amp requirements before connecting them to your generator.
Key Points
Understanding amps is key when choosing and using diesel or petrol generators. They determine how much current flows to your devices, helping you prevent overloads and ensure smooth operation.
By knowing how amps relate to watts and volts, you can calculate your power needs accurately and pick the right generator size. Whether you’re powering a worksite, home appliances, or industrial equipment, getting your amp calculations right will save you from power failures and electrical damage.

